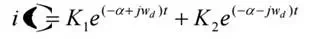Details about the step response of series RLC circuit
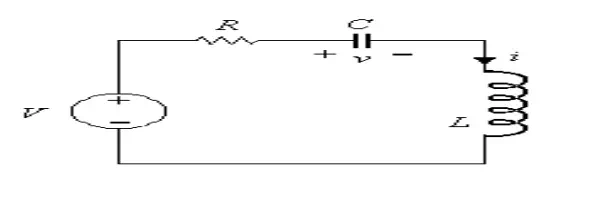
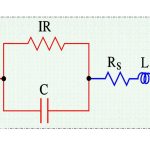
In series RLC circuit, there are two energy storing element which are L and C, such a circuit give rise to second order differential equation and hence called second order circuit. Consider a series RLC circuit shown in Figure. The switch is closed at t = 0 and a step voltage of V volts gets applied to circuit.
Apply KVL after switching we get
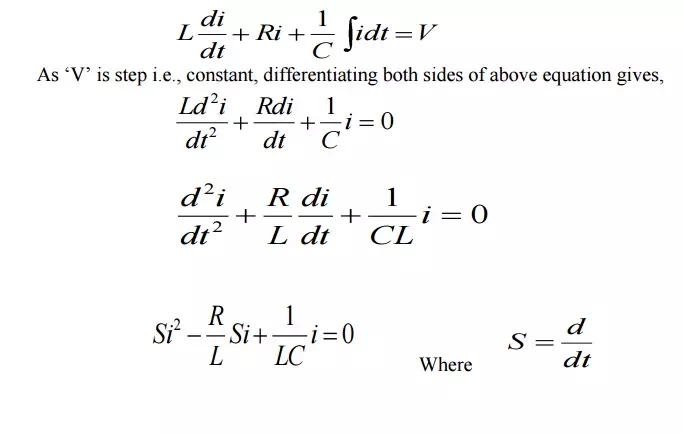
This is called characteristic equation or auxiliary equation of series RLC circuits. The response of the circuit depends on the nature of the roots of characteristic equation. The two roots are,
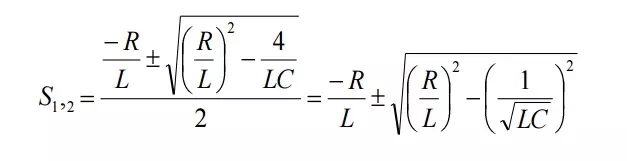
Let us define some quantities to find the response according to the nature of roots.
Critical resistance :-
This is the value of resistance which reduces square root term to zero, giving real, equal and negative roots.
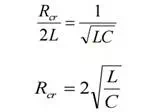
Damping Ratio (ξ):-
The ratio is the indication of opposition from the circuit to cause oscillations in its response more the value of this ratio, less are the chances of oscillations in the response. It is the ratio of actual resistance in the circuit to critical resistance.
It is denoted by zeta(ξ),
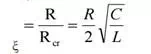
Natural: (ω)
If the damping is made zero then the response oscillates with natural frequency without any opposition. Such a frequ Frequency of oscillations,.Itisgivenby denoted as ω
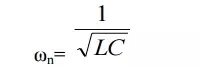
Using these values, the roots of equation are
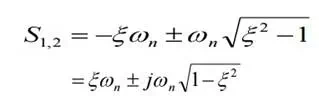
Thus the response is totally dependent on the Let n α = ξ ω
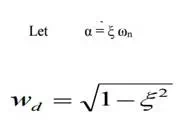
Where wd = actual frequency of oscillations (i.e) damped frequency when ξ = 0,
wd = ωn (i.e.) natural frequency.
The general solution of characteristic equation is