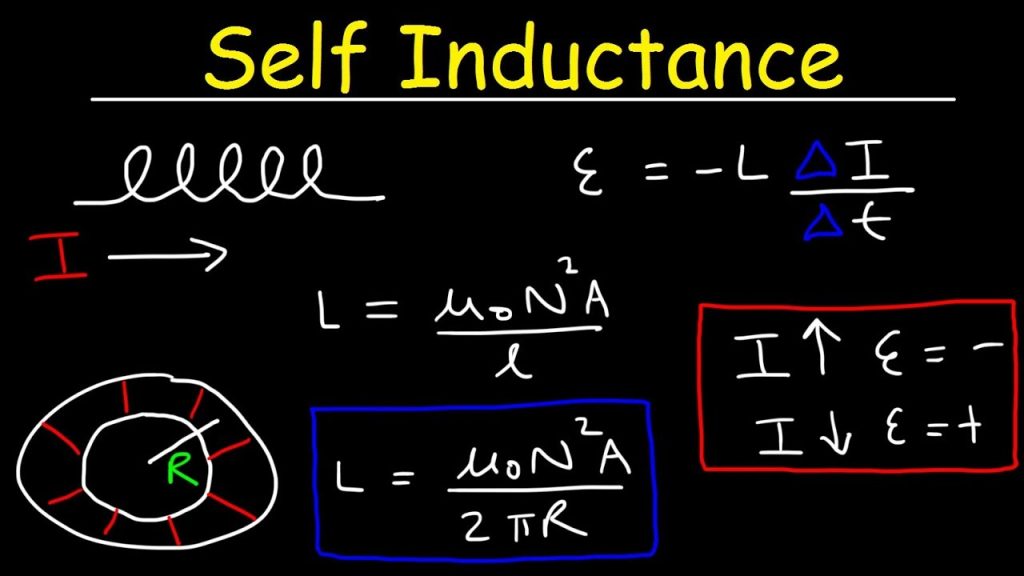
If a coil is considered in which some current flows, it has some magnetic field, perpendicular to the current flow. When this current keeps on varying, the magnetic field also changes and this changing magnetic field, induces an EMF, opposite to the source voltage. This opposing EMF produced is the self-induced voltage and this method is called as self-inductance.

The current is in the figure indicate the source current while iind indicates the induced current. The flux represents the magnetic flux created around the coil. With the application of voltage, the current is flows and flux gets created. When the current is varies, the flux gets varied producing iind.
This induced EMF across the coil is proportional to the rate of change in current. The higher the rate of change in current the higher the value of EMF induced.
We can write the above equation as
EαdIdtEαdIdt
E=LdIdtE=LdIdt
Where,
· E is the EMF produced
· dI/dt indicates the rate of change of current
· L indicates the co-efficient of inductance.
Self-inductance or Co-efficient of Self-inductance can be termed as
L=EdIdtL=EdIdt
The actual equation is written as
E=−LdIdtE=−LdIdt
The minus in the above equation indicates that the EMF is induced in opposite direction to the voltage source according to Lenz’s law.