An Inductor when connected in a circuit, that connection can be either series or parallel. Let us now know what will happen to the total current, voltage and resistance values if they are connected in series as well, when connected in parallel.
Inductors in Series
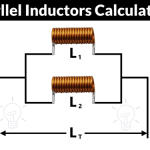
Let us observe what happens, when few inductors are connected in Series. Let us consider three resistors with different values, as shown in the figure below.

Inductance
The total inductance of a circuit having series inductors is equal to the sum of the individual inductances. Total inductance value of the network given above is
LT=L1+L2+L3LT=L1+L2+L3
Where L1 is the inductance of 1st resistor, L2 is the inductance of 2ndresistor and L3 is the inductance of 3rd resistor in the above network.
Voltage
The total voltage that appears across a series inductors network is the addition of voltage drops at each individual inductances.
Total voltage that appears across the circuit
V=V1+V2+V3V=V1+V2+V3
Where V1 is the voltage drop across 1st inductor, V2 is the voltage drop across 2nd inductor and V3 is the voltage drop across 3rd inductor in the above network.
Current
The total amount of Current that flows through a set of inductors connected in series is the same at all the points throughout the network.
The Current through the network
I=I1=I2=I3I=I1=I2=I3
Where I1 is the current through the 1st inductor, I2 is the current through the 2nd inductor and I3 is the current through the 3rd inductor in the above network.