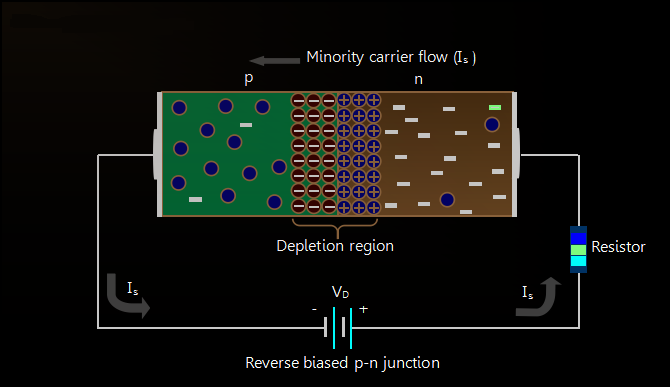
When an external voltage is applied to a diode such that it cancels the potential barrier and permits the flow of current is called as forward bias. When anode and cathode are connected to positive and negative terminals respectively, the holes in P-type and electrons in N-type tend to move across the junction, breaking the barrier. There exists a free flow of current with this, almost eliminating the barrier.

With the repulsive force provided by positive terminal to holes and by negative terminal to electrons, the recombination takes place in the junction. The supply voltage should be such high that it forces the movement of electrons and holes through the barrier and to cross it to provide forward current.
Forward Current is the current produced by the diode when operating in forward biased condition and it is indicated by If.