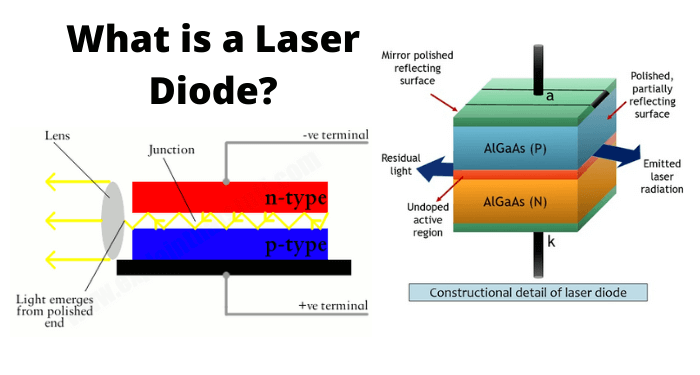
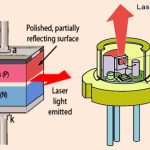
Whenever a photon is incident on an atom, that atom is excited from a lower energy state to a higher energy state and two photons are released in this process. Actually, an atom can generally stay at this excited state for 10-8 secs of time. So, in order to achieve amplification, during this excited process, the atom is made to be placed in another state called Meta Stable State which is below the higher energy level and above the lower energy level.
An atom can stay in this Meta stable state for 10-3 secs. While the atom gets to the lower state from this, two photons are released. If more number of atoms are there in the excited state, prior to the photons striking the atoms, then we have the Lasing Effect.

In this process, we have two terms to understand. Having more number of atoms at Meta Stable state than the lower energy state or ground state is called as Population inversion. Then energy that lets the atoms to send from a lower energy state to a higher energy state to achieve the population inversion, is called as Pumping. This is Optical pumping.

Advantages
There are many advantages of Laser diode such as −
- Power used by laser diodes is much less
- Higher ON/OFF switching speed
- More Compact
- Less expensive
- They are cheaper than laser generators
- Less chances of providing electrical shocks
Disadvantages
There are few disadvantages of Laser diode such as −
- More divergent rays and hence quality is not so good
- Their life time is less compared to LED.
- Prone to damage during unstable power supplies
Applications
There are many applications of Laser diode such as −
· Used as pump-laser and seed-laser
· Used in optical data storage devices
· Used in laser printers and laser fax machines
· Used in Laser pointers
· Used in bar-code readers
· They are used in DVD and CD drives
· Used in HD DVD and BLU RAY technology
· Has many industrial purposes such as heat treating, cladding, seam welding etc.
· Has got many uses in communication technology such as data linking and transmission.
After going through all these, let us try to understand few terms.
Component
- The Components are the individual basic elements of electronics.
- They have different properties with respect to their construction.
- Every component has different applications.
Ex − Resistor, Capacitor, Diode etc.
Circuit
- A Circuit is a network of different components
- The components in the circuit altogether, survive an intended purpose.
- If a circuit has to be active, should contain a power source.
Ex − clipper and clamper circuits, amplifier circuits, relay circuits etc.
Device
· A Device is an equipment that is made up of different circuits.
· All circuits in the device help it function to serve its purpose.
· A device can be used for measuring signals, generating signals, controlling the outcomes or protecting the circuits and so on.
Ex − CRO, Function generator etc.
Solid State devices
Previously we used to have vacuum tubes, which work on thermionic principle and are filled with vacuum inside. They were bigger in size than today’s components. These vacuum tubes were replaced with semiconductor devices, which are also called as Solid state devices.
Active Devices
The devices (or precisely components) which can control the current flow can be termed as Active Devices.
- They require some input power supply to get into conduction.
- The working of these components define the behavior of the circuit.
Ex − Vacuum tubes, diodes, transistors, SCRs
Passive Devices
The devices (or precisely components) which cannot control the current flow can be termed as Passive Devices.
- They don’t require input power supply to work.
- The working of these components slightly alters the circuit’s behavior.
Ex − Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor etc.
Doping
The process of adding of electrons or creating holes to alter the characteristics of the semiconductor material, either by making more positive or by making more negative can be understood as Doping.
The applications of diodes include many circuits starting from clipper and clamper circuits, which will be discussed in ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS tutorial.