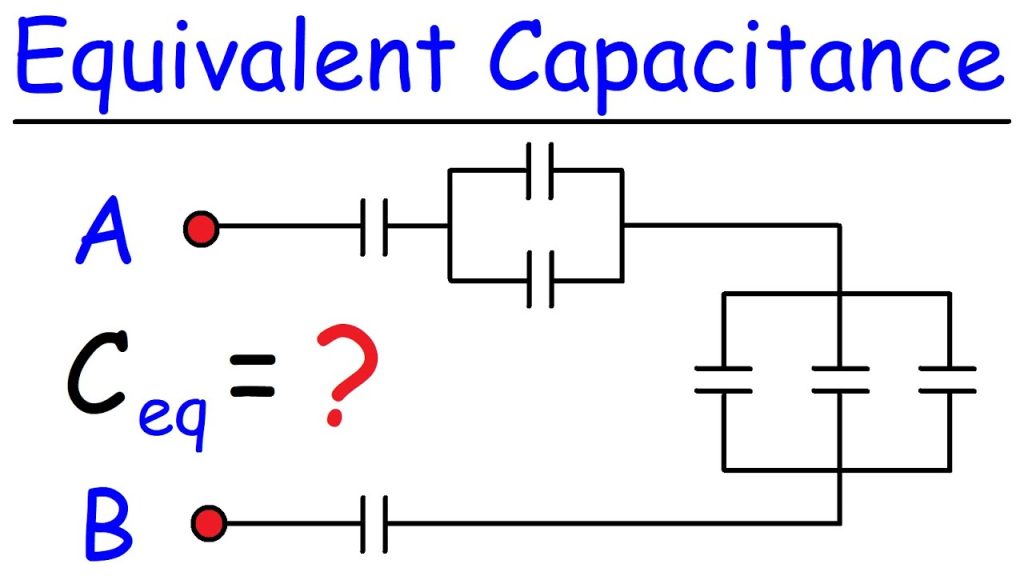
Capacitors
Every system of electrical conductors possesses capacitance. For example, there is capacitance between the conductors of overhead transmission lines and also between the wires of a telephone cable. In these examples the capacitance is undesirable but has to be accepted, minimized or compensated for. There are other situations where capacitance is a desirable property.
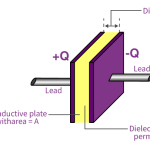
Devices specially constructed to possess capacitance are called capacitors (or condensers, as they used to be called). In its simplest form a capacitor consists of two plates which are separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. A capacitor has the ability to store a quantity of static electricity.
The symbols for a fixed capacitor and a variable capacitor used in electrical circuit diagrams are shown in Figure 6.4.



Hence the capacitor can provide an average discharge current of 2 mA for 2 s.