1. Single channel and Multi-channel signals
2. Single dimensional and Multi-dimensional signals
3. Continuous time and Discrete time signals.
4. Continuous valued and discrete valued signals.
5. Analog and digital signals.
6. Deterministic and Random signals
7. Periodic signal and Non-periodic signal
8. Symmetrical(even) and Anti-Symmetrical(odd) signal
9. Energy and Power signal
1) Single channel and Multi-channel signals
If signal is generated from single sensor or source it is called as single channel signal. If the signals are generated from multiple sensors or multiple sources or multiple signals are generated from same source called as Multi-channel signal. Example ECG signals. Multi-channel signal will be the vector sum of signals generated from multiple sources.
2) Single Dimensional (1-D) and Multi-Dimensional signals (M-D)
If signal is a function of one independent variable it is called as single dimensional signal like speech signal and if signal is function of M independent variables called as Multi-dimensional signals. Gray scale level of image or Intensity at particular pixel on black and white TV are examples of M-D signals.
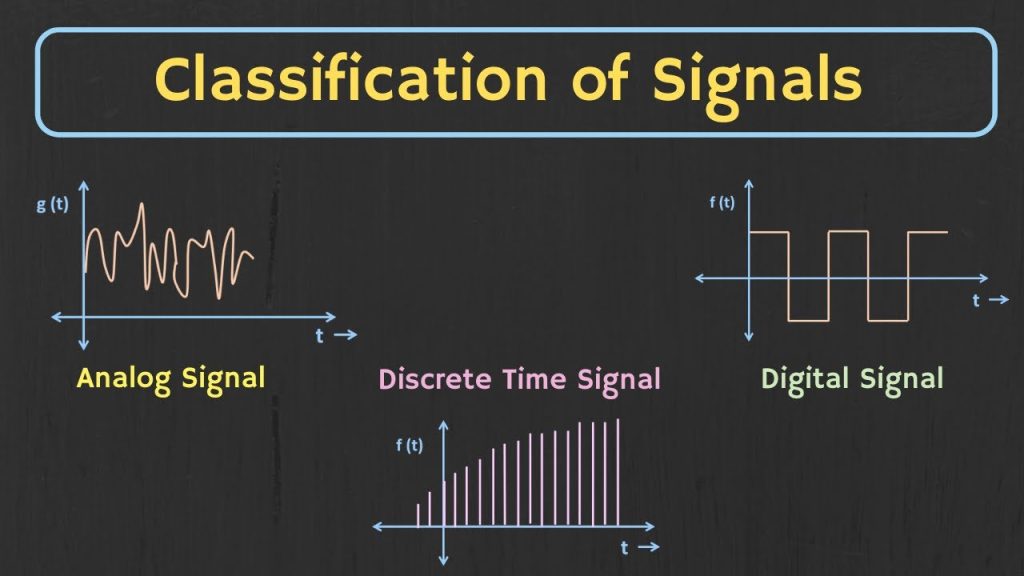
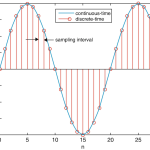
3) Continuous time and Discrete time signals.


4) Continuous valued and Discrete Valued signals

5) Analog and digital signal

Note: Digital signals (DISCRETE TIME & DISCRETE AMPLITUDE) are obtained by sampling the ANALOG signal at discrete instants of time, obtaining DISCRETE TIME signals and then by quantizing its values to a set of discrete values & thus generating DISCRETE AMPLITUDE signals. Sampling process takes place on x axis at regular intervals & quantization process takes place along y axis. Quantization process is also called as rounding or truncating or approximation process.
6) Deterministic and Random signals

7) Periodic signal and Non-Periodic signal
The signal x(n) is said to be periodic if x(n+N)= x(n) for all n where N is the fundamental period of the signal. If the signal does not satisfy above property called as Non-Periodic signals. Discrete time signal is periodic if its frequency can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. f= k/N where k is integer constant.

8) Symmetrical(Even) and Anti-Symmetrical(odd) signal