The purpose of an Electric Power System is to generate and supply electrical energy to consumers. The power system should be designed and managed to deliver this energy to the utilization points with both reliability and economically
The capital investment involved in power system for the generation, transmission and distribution is so great that the proper precautions must be taken to ensure that the equipment not only operates as nearly as possible to peak efficiency, but also must be protected from accidents
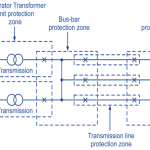
The normal path of the electric current is from the power source through copper (or aluminium) conductors in generators, transformers and transmission lines to the load and it is confined to this path by insulation. The insulation, however, may break down, either by the effect of temperature and age or by a physical accident, so that the current then follows an abnormal path generally known as Short Circuit or Fault
Any abnormal operating state of a power system is known as FAULT. Faults in general consist of short circuits as well as open circuits. Open circuit faults are less frequent than short circuit faults, and often they are transformed in to short circuits by subsequent events.

Consequences of occurrence of Faults