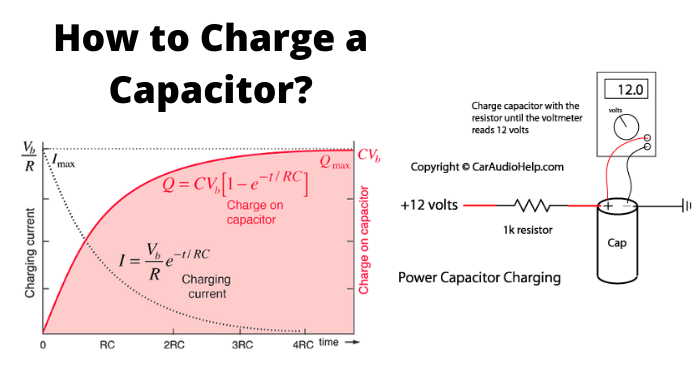
When an external voltage is given, the electric charge gets converted into electrostatic charge. This happens while the capacitor is charging. The positive potential of the supply, attracts the electrons from the positive plate of the capacitor, making it more positive. While the negative potential of the supply, forces the electrons to the negative plate of the capacitor, making it more negative. The figure below explains this.

During this process of charging, the electrons move through the DC supply but not through the dielectric which is an insulator. This displacement is large, when the capacitor starts to charge but reduces as it charges. The capacitor stops charging when the voltage across capacitor equals the supply voltage.

Let us see what happens to the dielectric when the capacitor begins to charge.