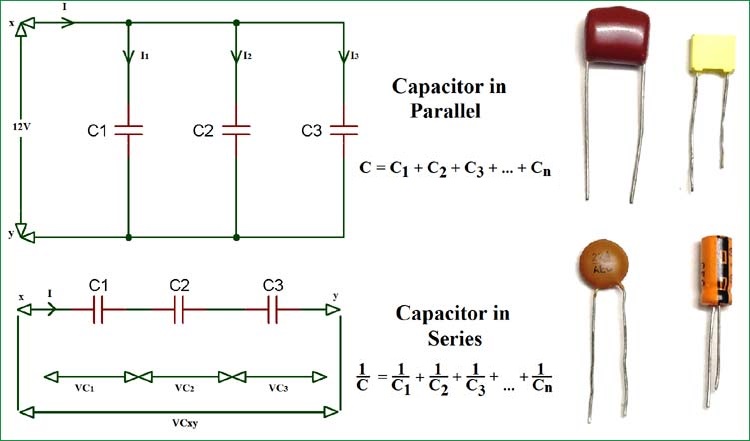
In a circuit, a Capacitor can be connected in series or in parallel fashion. If a set of capacitors were connected in a circuit, the type of capacitor connection deals with the voltage and current values in that network.
Capacitors in Series
Let us observe what happens, when few Capacitors are connected in Series. Let us consider three capacitors with different values, as shown in the figure below.

Capacitance
When the capacitance of a network whose capacitors are in series is considered, the reciprocal of the capacitances of all capacitors, is added to get the reciprocal of the total capacitance. To get this more clearly,
1CT=1C1+1C2+1C31CT=1C1+1C2+1C3
Following the same formula, if simply two capacitors are connected in series, then
CT=C1×C2C1+C2CT=C1×C2C1+C2
Where C1 is the capacitance across the 1st capacitor, C2 is the capacitance across the 2nd capacitor and C3 is the capacitance across the 3rd capacitor in the above network.
Voltage
The voltage across each capacitor depends upon the value of individual capacitances. Which means
VC1=QTC1VC2=QTC2VC3=QTC3VC1=QTC1VC2=QTC2VC3=QTC3
The total voltage across the series capacitors circuit,
VT=VC1+VC2+VC3VT=VC1+VC2+VC3
Where Vc1 is the voltage across the 1st capacitor, Vc2 is the voltage across the 2nd capacitor and Vc3 is the voltage across the 3rd capacitor in the above network.
Current
The total amount of Current that flows through a set of Capacitors connected in series is the same at all the points. Therefore the capacitors will store the same amount of charge regardless of their capacitance value.
Current through the network,
I=I1=I2=I3I=I1=I2=I3
Where I1 is the current through the 1st capacitor, I2 is the current through the 2nd capacitor and I3 is the current through the 3rd capacitor in the above network.
As the current is same, the storage of charge is same because any plate of a capacitor gets its charge from the adjacent capacitor and hence capacitors in series will have the same charge.
QT=Q1=Q2=Q3QT=Q1=Q2=Q3