The two most significant semiconductor light emitting sources extensively used in various applications are LASER diodes and LED’s. The principle operation of LASER diodes is based on stimulated emission, whereas LED is based on spontaneous emission.
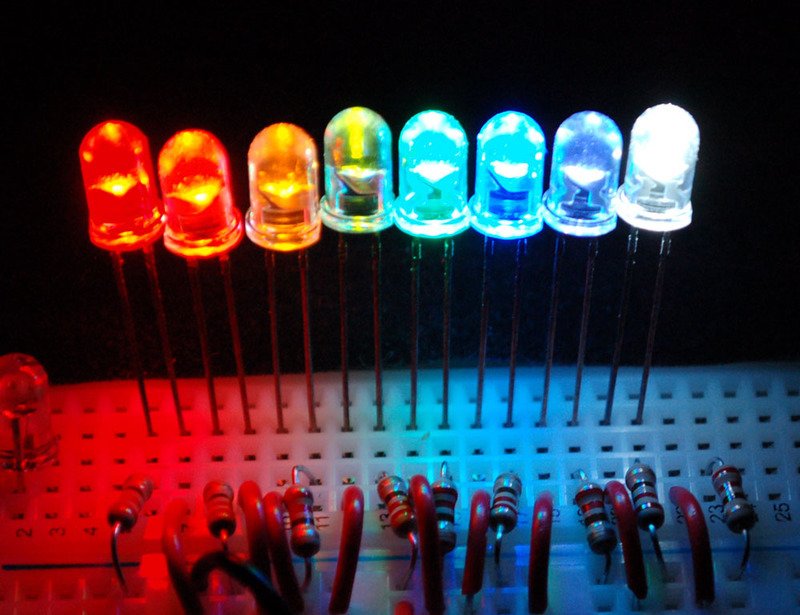
The most common eminent source of light available in electronic components are Light Emitting Diodes. For instance, they are widely used for displaying the time and many other types of data on screens in certain display devices. LED’s are the opto – semiconductor devices which easily converts electric current into illumination (or light). Area of the LED is usually less than 1 and many integrated optical components may be used in designing its radiation pattern. It has the major advantage of low manufacturing cost and renders longer life than the laser diode. A light emitting diode consists of two principal elements of semiconductor. They are positively charged P-type holes and negatively charged N-type electrons.
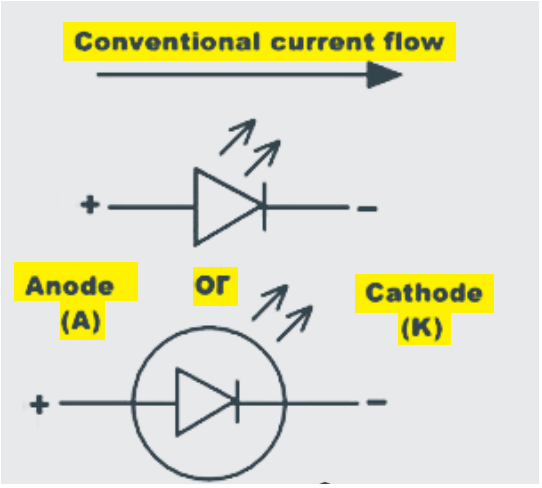
When the positive P side of the diode is connected to power supply, and N side to the ground, then the connection is said to be in forward bias which allows the electric current to flow through the diode. The majority and minority charge carriers of P side and N side combine with each other and neutralize the charge carriers in the depletion layer at the PN junction. The migration of electrons and holes in turn releases some amount of photons which discharges energy in the form of monochromatic light at a constant wavelength usually in nm, which resembles the color of an LED. The color spectrum of LED emission is typically extremely narrow.
In general, it can be specified as a certain specific range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. The selection of emission of color from the LED is fairly limited due to the nature of semiconductor used in the manufacture. Commonly available colours of LED are red, green, blue, yellow, amber and white. The light from red, blue and green colours can be easily combined to produce white light with limited brightness. The working voltage of red, green, amber and yellow colors is around 1.8 volts. The actual range of working voltage of a light emitting diode can be determined by the breakdown voltage of semiconductor material involve in the construction of LED. The colour of the light emitted in LED is determined by the semiconductor materials that form the diode’s PN junction.
It is due to the differences in the energy gap band structure of semiconductor materials and so different number of photons is emitted with varying frequencies. However the wavelength of light depends on the band gap of the semiconductor materials at the junction and the intensity of light depends on the amount of power or energy applied through the diode. The output wavelength can be maintained by using compound semiconductors, so that required color can be observed, providing the output within the visible range.
Light can be produced and controlled by electronic means in a number of ways. In light emitting diodes, light is produced through the concept of electroluminescence which is a solid state process. Under certain specific conditions of producing the light, solid state procedures can produce a coherent light, similarly as in laser diodes.