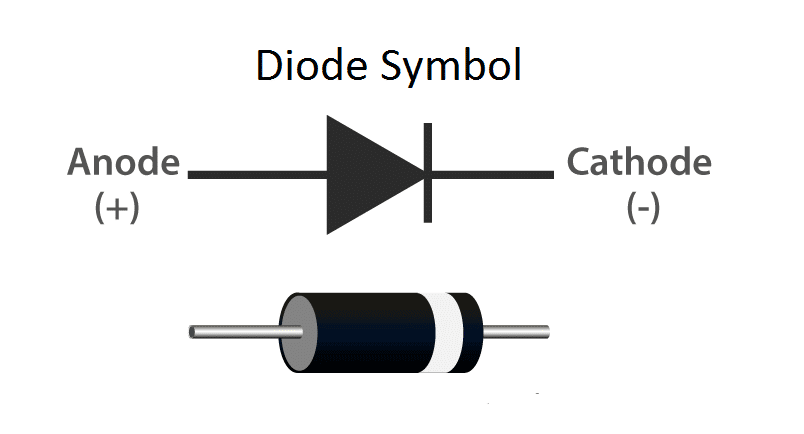
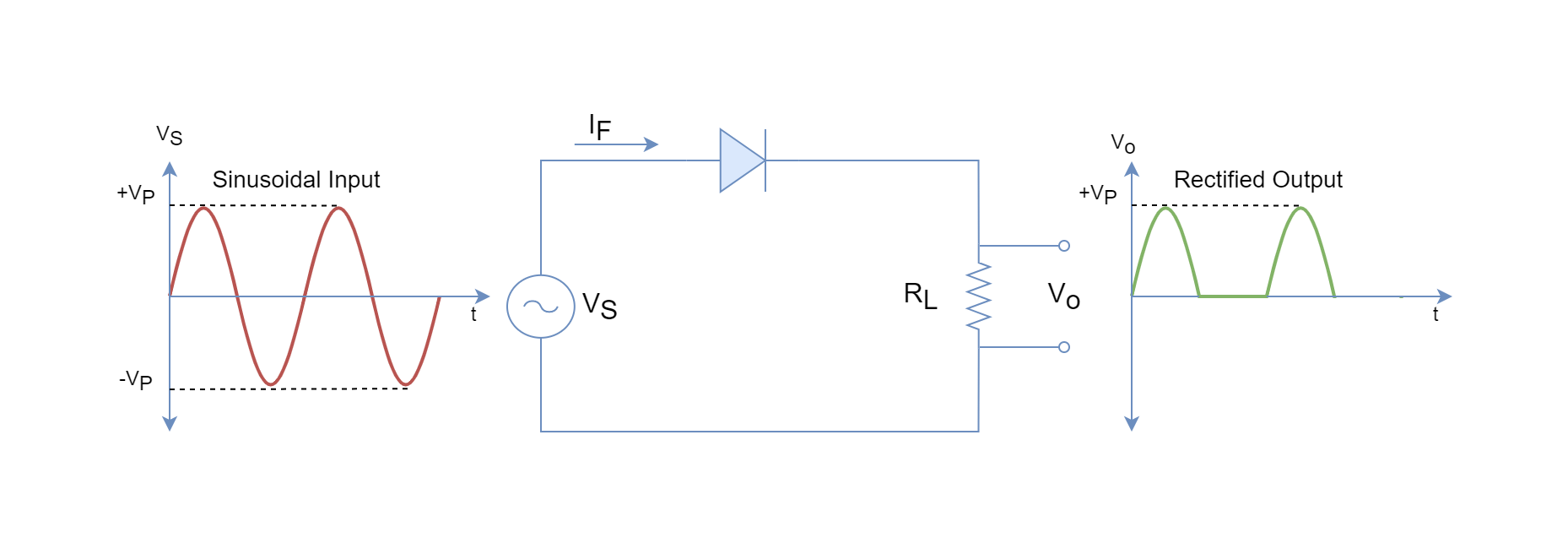
We know that small signal diodes are used in several applications like current steering, over voltage protection, switching circuits, clipping circuits, clamping circuits, snubbing the small duration waveforms and the most important of all: power conversions (from AC to DC). Small signal diodes conduct current solely in one direction: from anode to cathode and this is the most important property used in converting alternating current to direct current. This process of current conversion is called as Rectification and the circuits used are called Rectifiers.
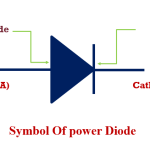
But due to the large amounts of forward current and revere bias voltage, small signal diodes may be overheated and get damaged in the process of rectification. In such cases, Power Semiconductor Diodes are used to overcome the excess currents and voltages.
A Power Semiconductor Diode is a crystalline semiconductor device, also known as Power Diode, used mainly for the purpose of rectification. This type of rectification process is mostly seen in all power supplies of modern-day electronic and electrical apparatus. Similar to small signal diodes, a power diode also conducts current only in one direction which is regarded as its forward direction, but doesn’t conduct current in the reverse direction. Power diode’s function seems to be analogous to a mechanical/electrical one-way valve.
Power diodes have very much larger P-N junction area, as a result, they have higher forward bias current carrying capacity than the smaller semiconductor signal. Power diodes are typically capable of passing several kilo amps (KA) of forward current and several kilo volts (KV) of reverse voltage. This makes power diodes better suited for applications where large amounts of currents and voltages are of concern than their small signal or low power counterparts.
Power diodes can be rated based on their two important characteristics: the maximum current that they can be able to carry in the forward direction and the greatest amount of reverse bias voltage they can withstand. Due to the ON resistance of the power diode, a small voltage drop occurs during the conduction of current. On the other hand, a power diode can withstand a definite amount of reverse bias voltage before the breakdown condition where it ceases to function.