In Direct Current (DC), the flow of electric charge is unidirectional. In DC, the voltage and current maintain a constant polarity and direction. The source of direct current is the battery. On the other hand, in Alternating Current (AC), the flow of electric charge reverses direction periodically. In AC, the voltage changes polarity from positive to negative and vice versa over a period of time.This change in the polarity of the voltage is because of the change in the direction of current.AC is the supply used to power up the households, offices, industries, etc.Even though sine wave is the most common form of AC supply, some applications use different wave forms like triangular wave, square wave and sawtooth wave.
The most common form of AC supply is sinusoidal wave. The mathematical function describing a typical AC voltage is
V (t) = VMax sin ωt.
V (t) is the voltage in the function of time. The voltage changes with time.
t is the variable time in seconds.
VMax is the peak value that the sine wave can reach in both positive and negative directions. For positive cycle it is VMax and for negative cycle it is -VMax.
ω is the angular frequency. ω = 2πf.
f is the frequency of the sine wave.
In DC circuits, the calculation of current, voltage and power is carried out using Ohm’s law. Here the polarities of both voltage and current are assumed to be constant.
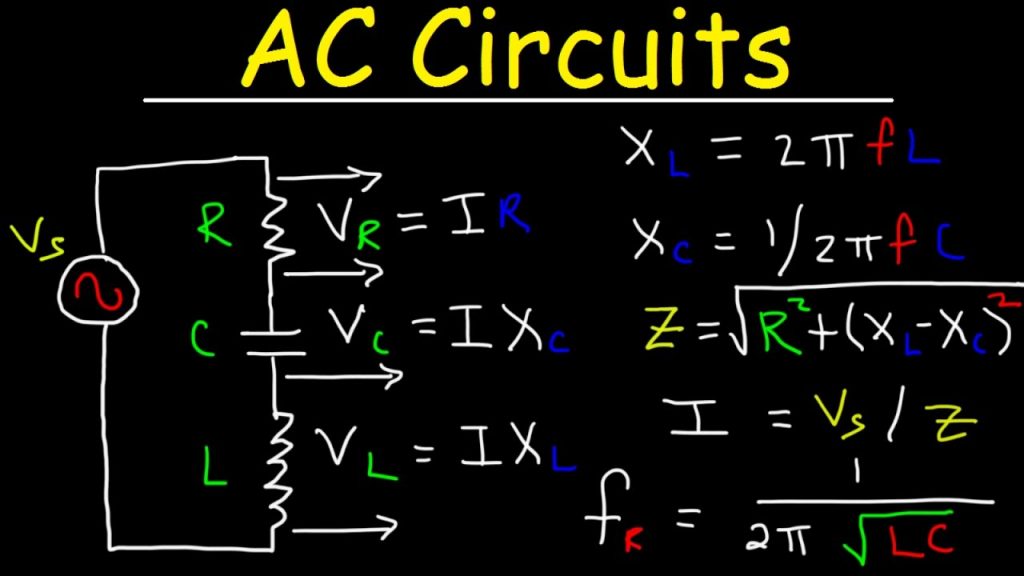
In case of pure resistive AC circuits, the values of inductance and capacitance are negligible. Hence the calculation of current, voltage and power will follow the same principles of Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s Circuit laws. The difference is in the use of instantaneous peak to peak value or rms value.
Resistor with DC and AC Supplies
Resistor is a passive device. It does not consume orproduce any energy. Energy here is electrical energy. But resistor dissipates electrical energy in the form of heat.
A resistor with a DC power supply is given below

In DC resistive circuits, the resistance which is the ratio of voltage to current is linear.
A resistor with an AC power supply is given below

In AC circuits, the voltage to current ratio is mainly dependent on supply frequency f and phase angle orphase difference φ. Hence the term Impedance is used in AC circuits to denote the resistance as it possess both magnitude and phase in contrast to the resistance in DC circuits where is possessed only magnitude. The symbol of impedance is Z.
V-I Phase Relationship in a Pure Resistive AC circuit
The resistance value of the resistor in both AC and DC circuits is same irrespective of the frequency of the AC supply voltage. The change in direction of current in AC supply does not affect resistors behavior. So the current in the resistor will rise and fall according to the voltage as it rises and falls.
The voltage and current in AC resistive circuit reach maximum, then fall to zero and reach minimum at the same time. They are said to be “in phase” as they rise and fall at exactly the same time.
Consider the following AC circuit.

Here the current is I (t) = IMax sin ωt.
The voltage V (t) = VMax sin ωt. => V (t) = IMax R sin ωt.
As the circuit is purely resistive, the effects of inductance and capacitance are negligible and the phase difference is 0.
Hence the relationship between the voltage and current in a resistor which is a part of resistive AC circuit is

The instantaneous values of currents and voltages are “in phase” along the x- axis of the curve. They rise and fall at the same time and reach their maximum and minimum values exactly at the same time.